PLASIMO's Drift-Diffusion module has been used to study and develop new plasma-based technology for the next generation of molecular decontamination systems [1]. The goal is to find an efficient plasma solution for decontamination of a carrier box by generating voluminous uniform low temperature plasma inside the box. The task is to use efficiently the plasma fluxes directed to the walls and in the same time to not damage surfaces of the box.
The object be treated here is a polycarbonate box with open top site and dimensions 30 cm x 30 cm x 30 cm. The box is placed on top of a grounded plate electrode. The powered electrode enters from the top inside the box. The applied voltage has a sinusoidal shape with amplitude of 300 V and a frequency of 33 kHz. The operating gas is argon at pressures in the range 0.45–1.45 mbar. At these operating conditions, the plasma is a typical dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) in the glow regime.
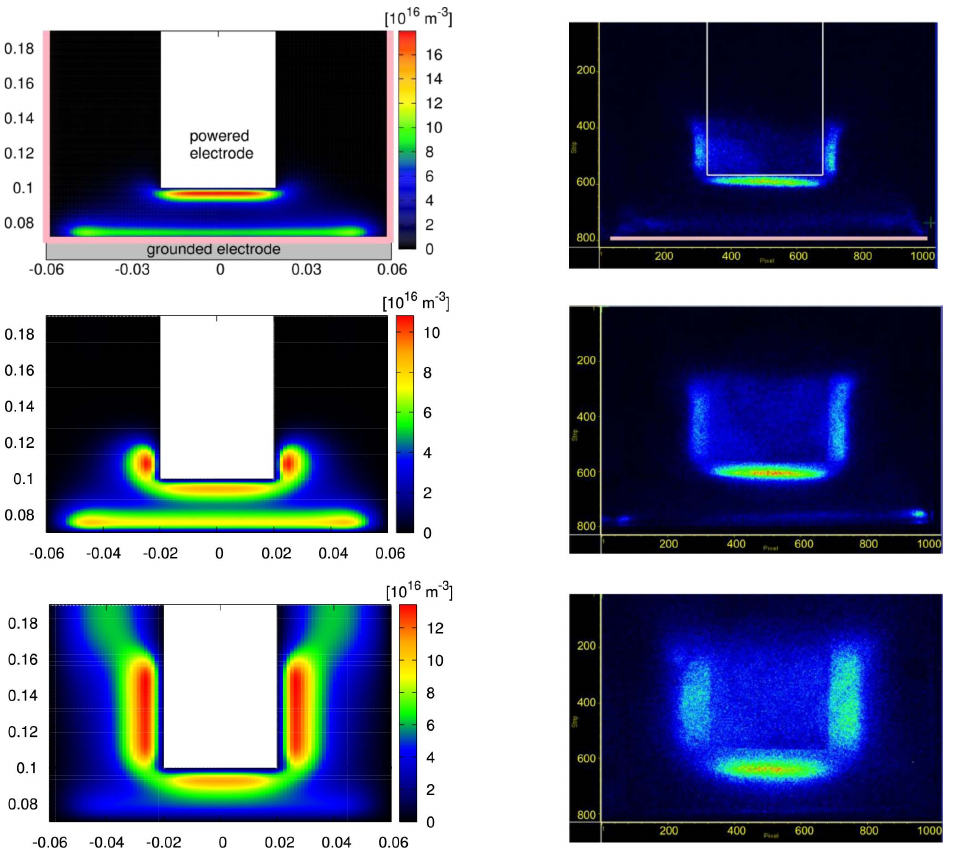
Figure 1. Calculated plasma density inside the box (first column) and the measured emission intensity (second column) at three different values of the gas pressure: 1.45, 0.8, and 0.45 mbar. On the top left figure, the geometry is marked: the polycarbonate box (pink), the grounded electrode below (gray), and the powered electrode (white) enters from top inside the box. Positions in the left column have been expressed in m, and in the right column in pixels.
References
[1] Mihailova D.B., Dijk J. van, Hagelaar G.J.M., Belenguer P. and Guillot P. (2014). Modelling of Low Temperature Plasma for Surface and Airborne Decontamination IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 42(10), 2760