PLASIMO’s Particle Growth Model describes the spatially averaged time-dependent nucleation, coagulation, charging and surface growth of dust particles due to one or more nucleation species.
The nucleation describes the onset of the particle growth process and typically corresponds to nucleation species formed due to the plasma activities. The coagulation processes are described in a sectional approach, meaning that the mass distribution is given by discrete mass values. A continuity equation is solved for each mass. Each mass can have a charge distribution and for each mass-charge combination one equation is solved. The charging of the particles due to collisions with electrons and ions is calculated using the collision frequencies from the orbital motion limited (OML) theory. Surface growth is assumed to take place via the ion collisions.
Example: Particle growth in acetylene plasma
The model describes the charge resolved mass coagulation, corresponding to an acetylene (C2H2) plasma. The considered nucleation species is C12H2 with 15 additional mass species that are formed from it.
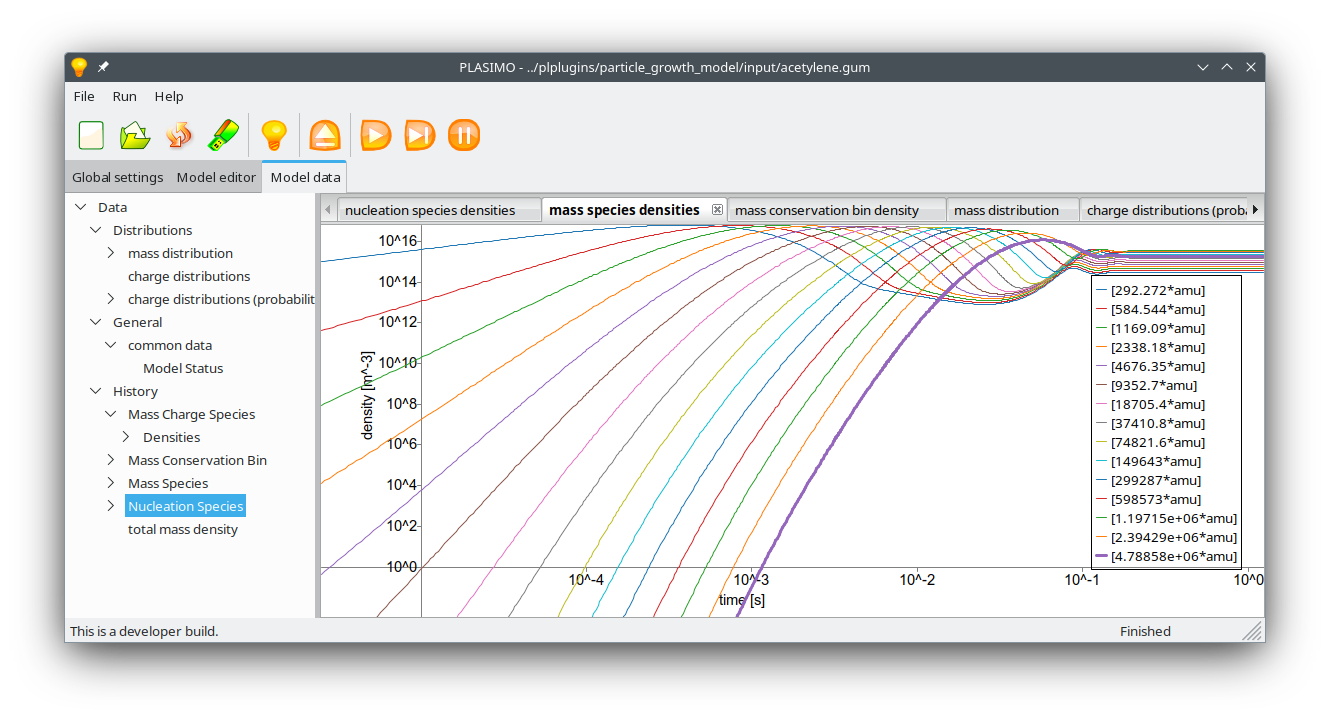
Figure 1: Calculated mass densities as a function of time.
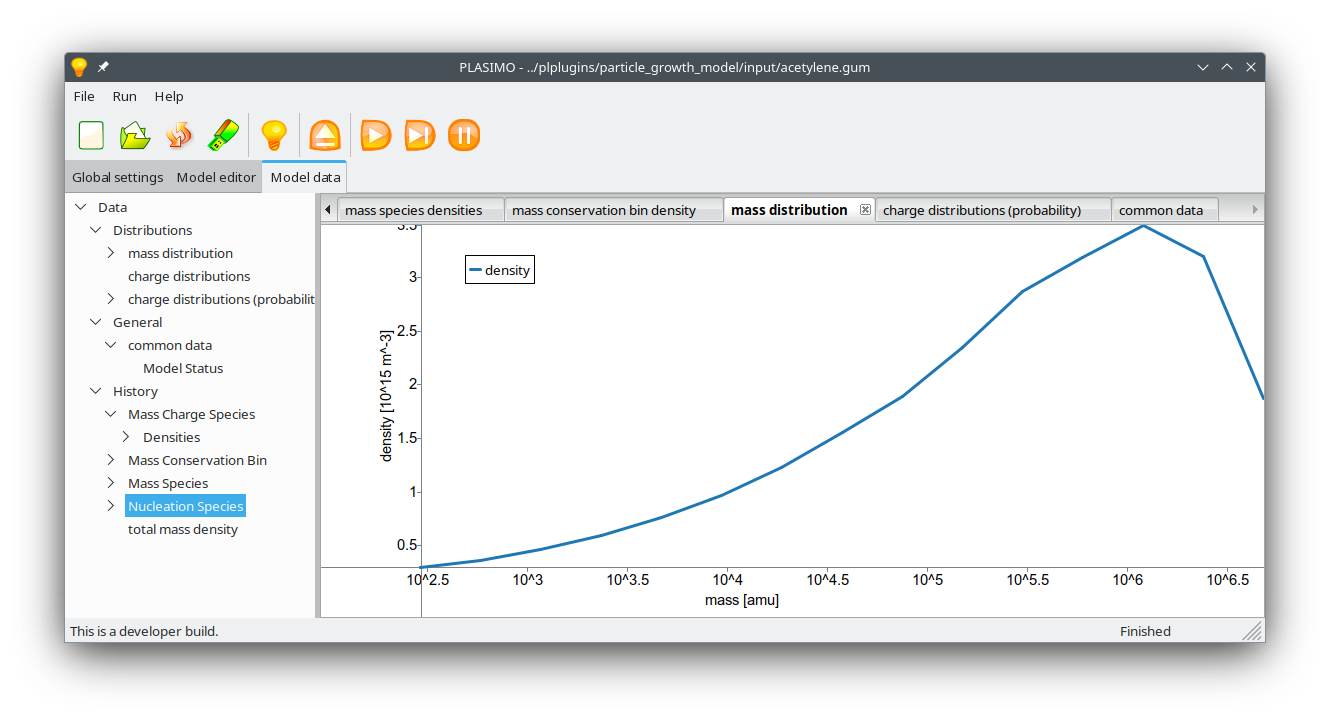
Figure 2: Calculated mass distribution after 1 second of particle growth.
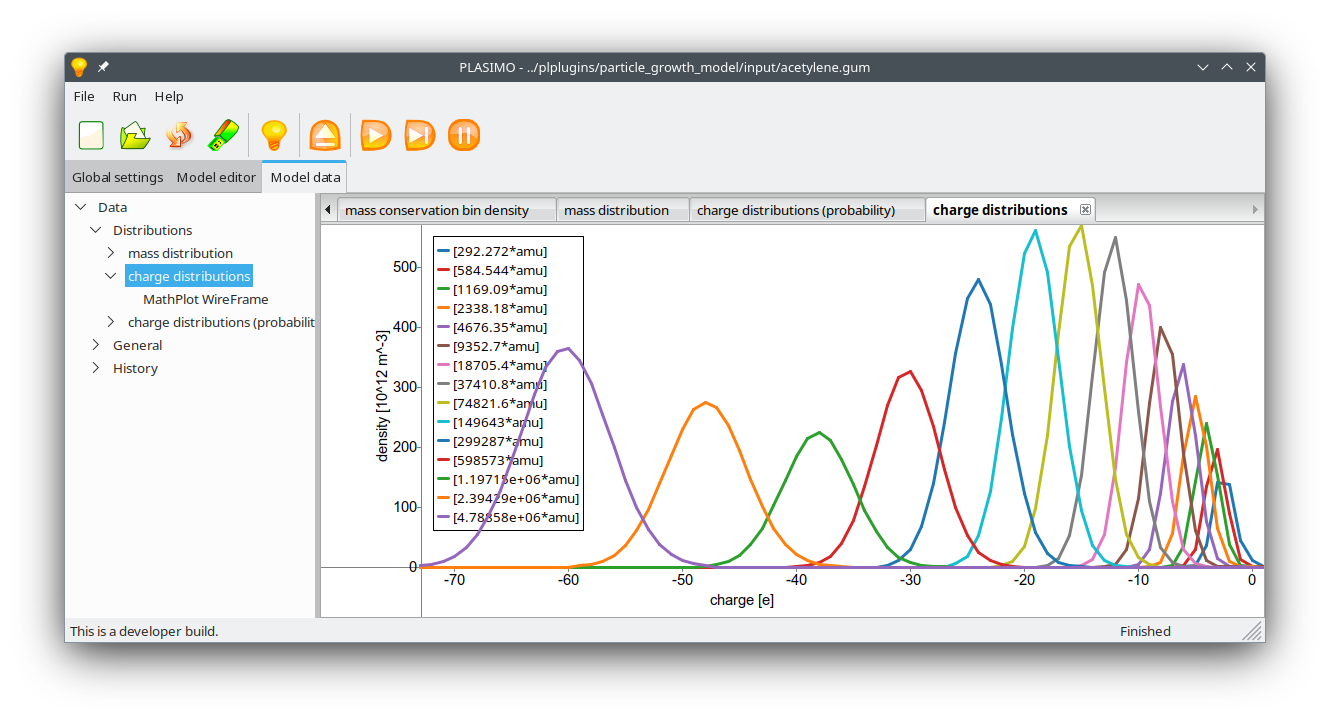
Figure 3: Calculated charge distribution per mass species after 1 second of particle growth.